Table of Content
- What Is Robots.txt?
- What Is a Search Engine Crawler?
- What is a User Agent in Robots.Txt?
- Format of Robots.txt
- What is Disallow in Robots.txt?
- What is Allow in Robots.txt?
- How to Block AI Crawlers?
- How to Create Robots.txt File?
- Where to Add Robots.txt File?
- How to Submit Robots.txt?
- How to Test Robots.txt File?
- Robots.txt vs Meta Robots Tag Comparison
- Steps to Setup & Robots.txt and Example
- Conclusion
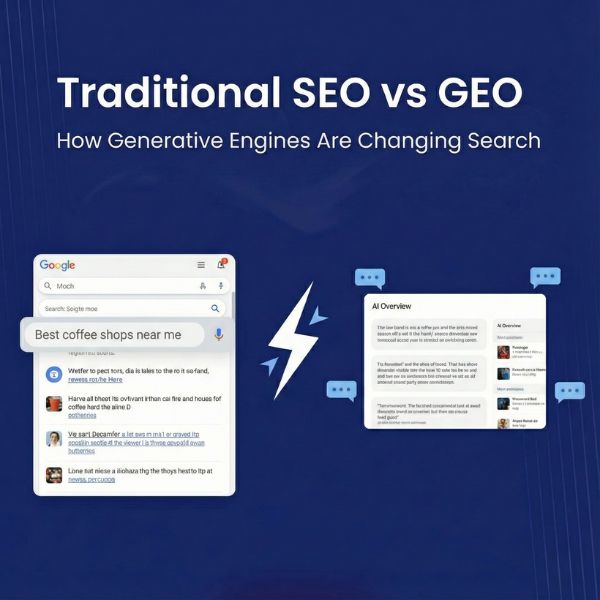
In SEO, visibility is everything. Search engines act as the gatekeepers of the web, deciding which pages deserve attention. But behind the scenes, a small yet mighty file quietly guides these bots – the robots.txt file.
This simple text file helps you control how search engine crawlers interact with your site – deciding what to index, what to ignore, and how deep they can go.
Whether you’re aiming to improve crawl efficiency, protect sensitive directories, or boost SEO performance, mastering robots.txt is a must.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
- What the robots.txt file is and how it works
- Key directives like Allow and Disallow
- How to block or allow AI crawlers
- Examples and best practices for perfect configuration
What Is Robots.txt?
A robots.txt file is a small text file located in the root directory of your website. It tells search engine crawlers which parts of your site they are allowed or disallowed to access.
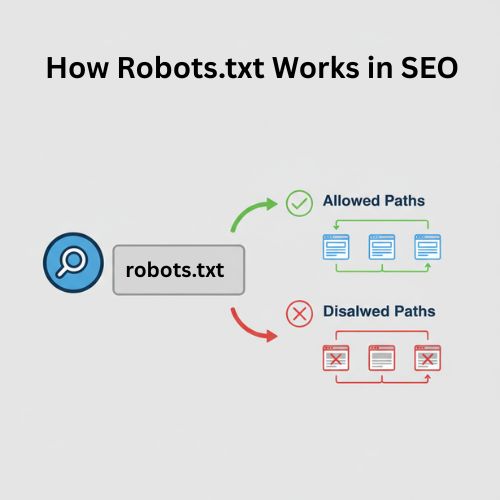
Its main purpose is to control crawler behavior and prevent unnecessary strain on your server from excessive bot requests.
✅ Important note: Most major search engines including Google, Bing, and Yahoo respect robots.txt directives. However, robots.txt doesn’t guarantee that blocked pages won’t appear in search results if they’re linked from other sites in some search engines.
What Is a Search Engine Crawler?
A search engine crawler (also called a spider or bot) is an automated program operated by search engines. Its job is to discover, scan, and index web pages across the internet so they can appear in search results.
These crawlers follow links from one page to another, building a complete picture of your website’s structure and content – a process that plays a crucial role in a technical SEO audit. Understanding how these bots navigate your site helps you identify crawlability issues, broken links, or structural problems that may surface during a technical SEO audit.
List of Search Engine Crawlers
There are numerous types of search engine crawlers; here is a list of some of them:
- GoogleBot: This is Google’s standard web crawling bot used for their search engine.
- Bingbot: This is a general web crawling bot from the Bing search engine.
- Slurp: This is a web crawler bot from the Yahoo search engine.
- Baiduspider: This is a bot from a Chinese search engine called Baidu.
- YandexBot: This is a bot from a Russian search engine called Yandex.
- SearchGPT: This is a ChatGPT’s bot used to link to and surface websites in search results in ChatGPT ‘s search features.
- ChatGPT-User: This is for user actions in ChatGPT and Custom GPTs.
- PerplexityBot: This is designed to surface and link websites in search results on Perplexity.
- AnthropicBot: This is an AI-driven web crawler developed by Anthropic.
List of Google Crawlers
Now, have a look at the list of Google’s search engine bots:
- GoogleBot: Used for general web crawling
- GoogleBot-Image: This crawls images
- GoogleBot-News: This crawls news content
- GoogleBot-Video: This crawls video content
- GoogleBot-Mobile: This crawls mobile content
What is a User Agent in Robots.Txt?
A user agent identifies who or what is making a request to a website. For humans, it usually includes details about their browser and operating system. For bots, it indicates which type of crawler is visiting your site.
In a robots.txt file, you can target specific bots by using their user-agent names. For example, you could allow Googlebot to crawl a page while blocking Baiduspider.
Format of Robots.txt
The format of a robots.txt file is simple and follows a few basic directives:
- User-agent: defines the bot you want to target
- Disallow: tells bots which paths not to crawl
- Allow: specifies which pages or directories can be crawled
Basic format:
User-agent: [user-agent name]
Disallow: [URL path to block]
Allow: [URL path to allow]
What is Disallow in Robots.txt?
The disallow command is the most common in the robot exclusion protocol. It instructs bots to avoid accessing the webpage or group of pages specified after the directive.
The Disallow directive tells crawlers not to access a specific page or directory. It’s one of the most common commands in the robots.txt file.
Keep in mind, disallowed pages are not hidden from the public, users who know the direct URL can still access them.
Examples of Disallow in Robots.txt include:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
The above command prevents all search engines that respect robots.txt from crawling your website.
User-agent: *
Disallow:
The above command would allow all search engines to crawl your site by dropping a single character.
User-agent: googlebot
Disallow: /Photo
The command above prevents Google from crawling the ‘photo’ directory on your website, including all its contents.
What is Allow in Robots.txt?
The Allow directive tells crawlers which pages or directories they can access. It’s especially useful when you want to allow access to a specific page within a blocked directory.
⚠️ Not all search engines fully support the Allow command, so always test your robots.txt file after updating it.
How to Block AI Crawlers?
To block AI crawlers like ChatGPT, Claude AI, etc. in your robots.txt file, you need to identify their user-agent names and explicitly disallow them. However, blocking AI crawlers is generally not recommended due to the growing global reliance on AI technologies and trends.
Here’s how to do it:
User-agent: [AI crawler name]
Disallow: /
⚠️ Tip: Blocking AI crawlers may limit your site’s visibility in emerging AI-driven search platforms, so weigh the pros and cons before applying this.
How to Create Robots.txt File?
There are several ways to create a robots.txt file: you can either follow the step-by-step instructions provided by Google Search Central or use online tools to generate one easily.
You can create a robots.txt file manually or by using online robots.txt generators.
- Follow the format: plain text file named robots.txt
- Save it in UTF-8 encoding
- Use simple syntax (User-agent, Disallow, Allow)
For beginners, Google Search Central provides an easy step-by-step guide to create one correctly.
Where to Add Robots.txt File?
After successfully creating a robots.txt file, you should always place it in the root directory of your website. This is the top-level directory where your website’s main files are located.
For example:
https://www.example.com/robots.txt
When we go on the above address, a robots.txt file should be accessible. If you upload it elsewhere (like a subfolder), search engines won’t detect it.
How to Submit Robots.txt?
After creating and uploading your robots.txt file to the root directory of your website, you don’t need to manually submit it anywhere. Search engine crawlers automatically detect and fetch the file when they visit your site.
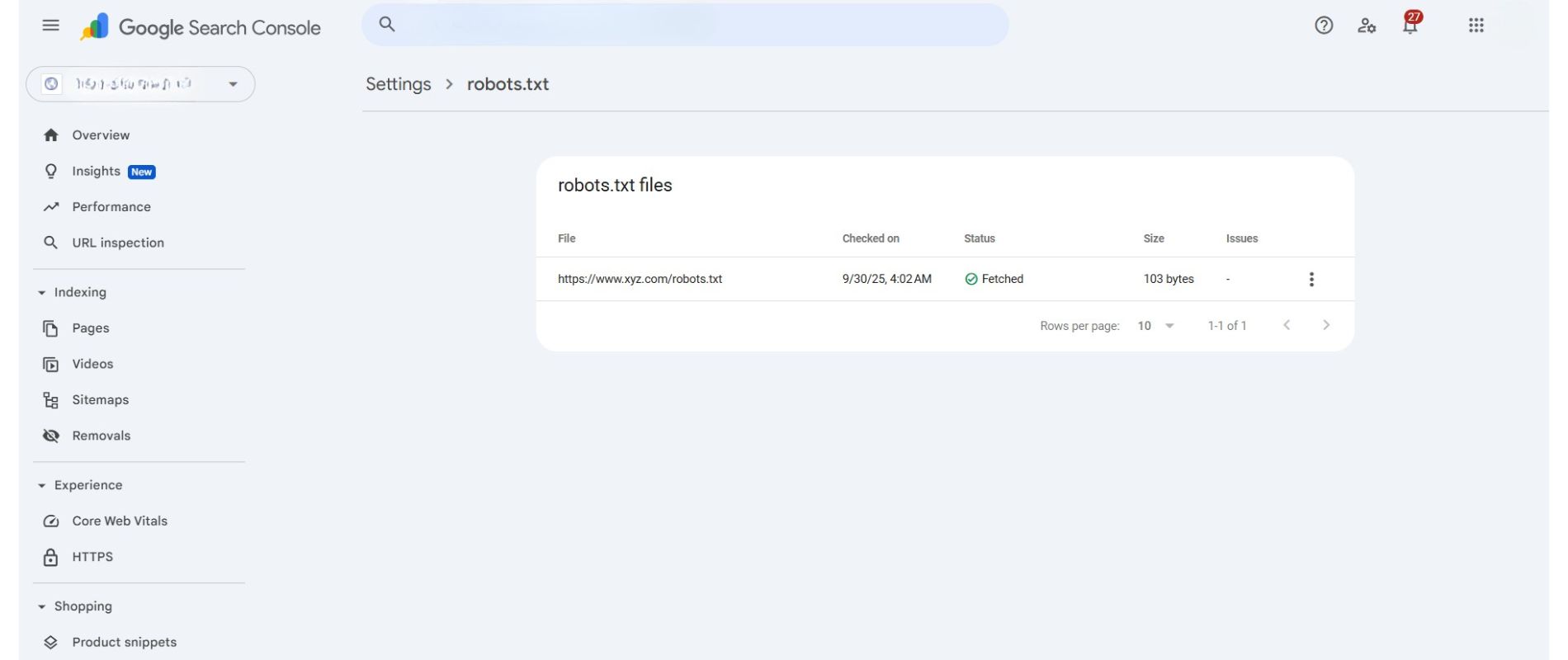
However, Google Search Console provides a helpful way to view and monitor your robots.txt status. Under Settings > robots.txt, clicking on “Open Report” shows you the current robots.txt URL, the last fetched content, the date and time of the last fetch, and its status (for example, Fetched or Failed).
This report helps you verify that search engines are accessing the correct file and lets you troubleshoot any issues, but the discovery and crawling process itself is fully automatic.
How to Test Robots.txt File?
To check whether your robots.txt is accessible or not, open a browser and switch to incognito mode, then navigate to the location of the robots.txt file.
For instance, http://abc.com/robots.txt. If you are able to view the contents of your robots.txt file, you’re ready to test the markup.
Google provides two methods for resolving issues related to robots.txt markup:
- The robots.txt report in Search Console is available only for files that are already publicly accessible on your website.
- If you are a developer, explore Google’s open-source robots.txt library, used by Google Search itself, which allows you to text robots.txt files locally on your computer.
- There are third party tools such as TechnicalSEO.com’s robots.txt Validator and Testing Tool
Robots.txt vs Meta Robots Tag Comparison
Robots.txt and Meta Robots tags guide search engines in handling site content but differ in their level of control, whether they are located, and what they control.
Consider these specifics:
- Robots.txt: This is the file that is located in the website’s root directory and provides site-wide instructions to search engine crawlers on which areas of the site they should and shouldn’t crawl.
- Meta Robots Tags: These tags are basically small code snippets placed in the <head> section of individual webpages, giving search engines specific instructions on whether to index the page (include it in search results) and follow its links (crawl them).
| Feature | Robots.txt | Meta Robots Tag |
| Location | Placed in the website’s root directory (e.g., /robots.txt) | Placed inside the <head> section of individual webpages |
| Scope | Site-wide control over crawler access | Page-level control over indexing and link following |
| Purpose | Tells crawlers which areas of the site they can or cannot crawl | Tells crawlers whether to index a page and follow its links |
| Affects | Crawling behavior | Indexing and link behavior |
| Example | Disallow: /private/ | <meta name=”robots” content=”noindex, nofollow”> |
| Use Case | Block entire directories or sections from being crawled | Control how specific pages appear in search results |
Steps to Setup & Robots.txt and Example
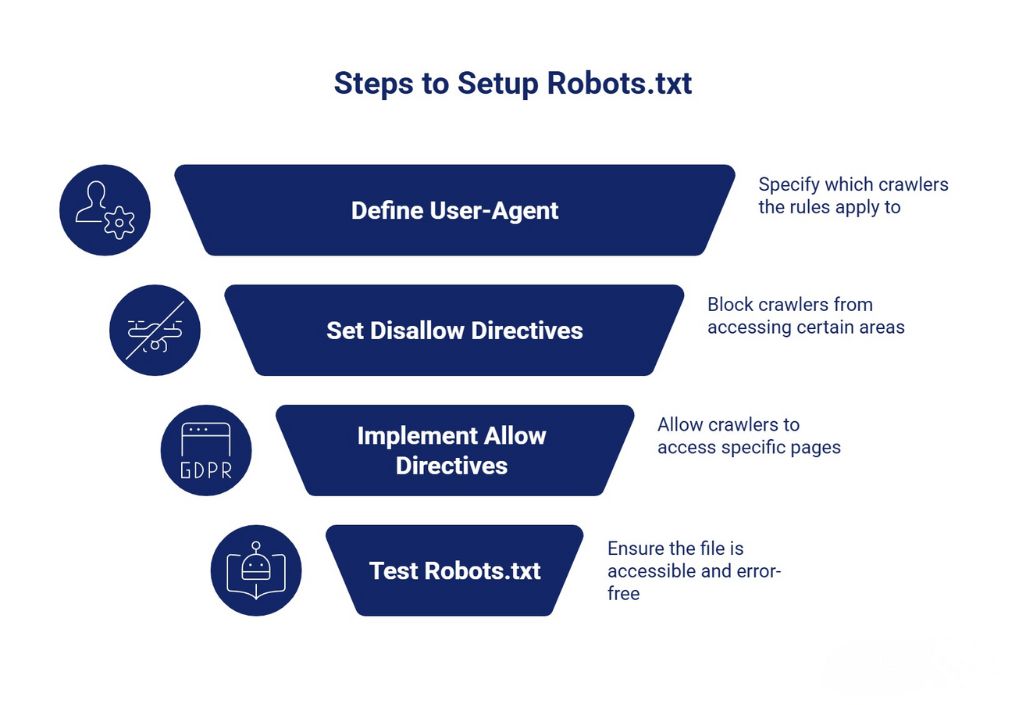
Many people search for examples of robots.txt files, and for a good reason, it’s easy to make mistakes when creating them. You can also check out our guide on what is sitemap to understand how both work together for better crawling and indexing.
Here’s an example of a simple robots.txt file
- Allows all crawlers access
- Lists the XML sitemap
User-agent: *
Disallow:
Sitemap: https://www.abc.com/sitemap.xml
Conclusion
From understanding what it is and how it works to learning how it controls search engine crawlers and improves crawl efficiency, we’ve covered all the essentials. If you have a large website or a small business site, configuring your robots.txt file correctly ensures search engines crawl your website the right way.
Ready to optimize your website’s technical SEO? At AONE SEO Service, best SEO company in Ahmedabad, we specialize in technical SEO audits, crawl budget optimization, website architecture improvements, and complete search visibility strategies tailored to your business goals.
📧 Email: info@aoneseoservice.com
📞 Call: +91 8101118111
💻 Or Contact Us
to get started.
Your website’s SEO success is just a click away!